| COCAMIDE
DIETHANOLAMINE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 68603-42-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 271-657-0 | |
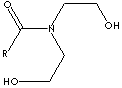
| FORMULA |
CH3(CH2)nC(=O)N(CH2CH2OH)2 |
|
| MOL WT. | 280 - 290 | |
| H.S. CODE |
|
|
| TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: > 3000 mg/kg |
|
| SYNONYMS | Coconut Oil Acid Diethanolamine Condensate; | |
| Coconut fatty acid amide of diethanolamine; Coconut diethanolamide; Cocamide DEA; coconut oil diethanolamine; n,n-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) cocoamide; n,n-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) coconut fatty acid amide; n,n-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) coconut oil amide; Coconut fatty acids diethanolamide; Coconut oil acids diethanolamide; Coconut oil acids, diethanolamine; Coconut oil diethanolamide; Coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide; Coconut oil fatty acids diethanolamide; coco-n,n-Bis(hydroxyethyl)amides; N,N-bis(hydroxyethyl)coco amides; n,n-bis(hydroxyethyl) coco fatty amides; coconut oil acid diethanolamine; cocamide diethanolamine; Diethanolamides of the fatty acids of coconut oil; | ||
| DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Viscous yellow liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | < 10 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 169 - 275 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.99 | |
|
pH |
9 (1% sol.) |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble | |
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| FLASH POINT | > 100 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Nonionic surfactants are surface active agents which do not dissociate into ions in aqueous solutions, unlike anionic surfactants which have a negative charge and cationic surfactants which have a positive charge in aqueous solution. Nonionic surfactants are more widely used as detergents than ionic surfactants because anionic surfactants are insoluble in many hard water and cationic surfactants are considered to be poor cleaners. In addition to detergency, nonionic surfactants show excellent solvency, low foam properties and chemical stability. It is thought that nonionic surfactants are mild on the skin even at high loadings and long-term exposure. The hydrophilic group of nonionic surfactants is a polymerized alkene oxide (water soluble polyether with 10 to 100 units length typically). They are prepared by polymerization of ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and butylene oxide in the same molecule. Depending on the ratio and order of oxide addition, together with the number of carbon atoms which vary the chemical and physical properties, nonionic surfactant is used as a wetting agent, a detergent, or an emulsifier. Nonionic surfactants include alcohol ethoxylates, alkylphenol ethoxylates, phenol ethoxylates, amide ethoxylates, glyceride ethoxylates (soya bean oil and caster oil ethoxylates), fatty acid ethoxylates, and fatty amine ethoxylates. Another commercially significant nonionic surfactants are the alkyl glycosides in which the hydrophilic groups are sugars (polysaccharides). Typically commercial coconut fatty acid has carbon chain composition of; C10 (5% max) + C12 (45 - 55%) + C14 (20 - 25%) + C16 (10 - 15 %) + C18 (10 - 15% max, including unsaturated fatty acids). Cocamide is an amide mixture of coconut fatty acids. Cocamides are manufactured by condensation of alkanolamines (mono-, di-, or triethanolamine) and coconut fatty acid. Examples are cocamide MEA (cocamide monoethanolamine), cocamide DEA (cocamide diethanolamine) and cocamide TEA (cocamide triethanolamine). They have the physical and chemical characteristics of alcohols, amines and long carbon chains in one molecule. Alkanolamides are nonionic surfactants impart excellent viscosity enhancing and foam stabilization in anionic based systems like hand washing liquids, shampoos, body cleansers and other personal care products. They act as lubricant agent, thickening agent and wetting agent. Their very good emulsifying property also provides applications in the field of pharmaceuticals, agricultural preparations, and textile processing; rust inhibiting, latex stabilizing, anti-static function in textiles, dye-leveling, waterproofing and water-in-oil additives as well as very good emulsifying. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Viscous yellow liquid | |
| ACTIVE MATTER |
83.0% max |
|
| FREE FATTY ACIDS |
0.5% max |
|
|
AMINE VALUE |
10 - 30 |
|
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max |
|
|
FREE OIL |
4.0% max |
|
|
OTHER CONTENT |
10.5% max (Glycerine) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER CAS RN | ||
|
8036-48-4; 8040-31-1; 8040-33-3; 12751-06-3; 53028-62-9; 56448-72-7; 56832-66-7;
63091-31-6; 66984-58-5; 67785-14-2; 67785-10-8; 71343-51-6;
71343-71-0; 83652-14-6;
90651-47-1; 118104-13-5;
|
||